Fix Low Memory warnings in Windows Vista, XP and Windows 7
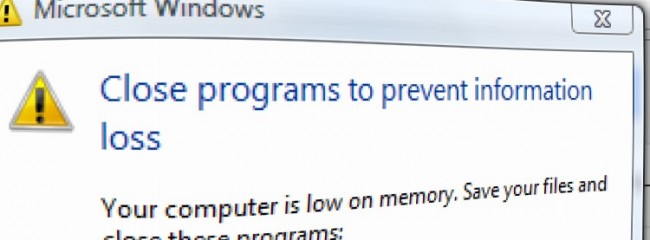
It can be one of the most annoying problems with Windows – you’re happily browsing the web or working on a document and suddenly up pops the “low-memory warning”.
Find out what causes this problem and how to fix it.
Low memory warnings happen when Windows has run out of space to put the data it needs to store when you’re running different applications. This can be either in the RAM modules in your computer, or also on the hard disk, when the free RAM has been filled up.
Typically if you’re getting these warnings, something has gone wrong with the paging file that uses your hard disk for extra storage.
You can check this by opening the Performance tab of Windows Task Manager (press the Ctrl-Alt-Del keys simultaneously).
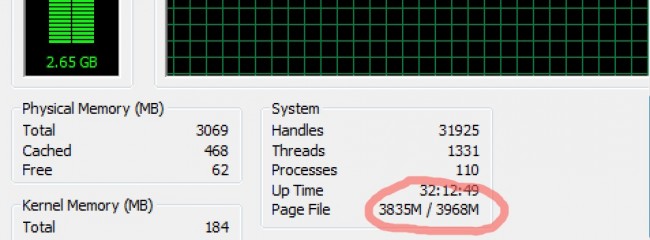
The page file is almost full – not good!
If your page file usage is almost full, and the Free memory is low, then Windows is running out of memory for your running applications.
This can cause things like web browser crashes, other program crashes etc.
How to fix it
- First, check that you have enough free disk space.You can usually do this by clicking on Computer from the Start Menu, and then looking at the free space value to the right of Local Disk.
If this is lower than a few hundred MB, then you need to free up space on the disk by deleting files, and then emptying the recycle bin. This will free up disk space for the paging file to use. - Your page file may be switched to manual instead of automatic control, and set to too low a value.
Check this by right-clicking on Computer and selecting Properties. You should get the system panel displayed similar to this: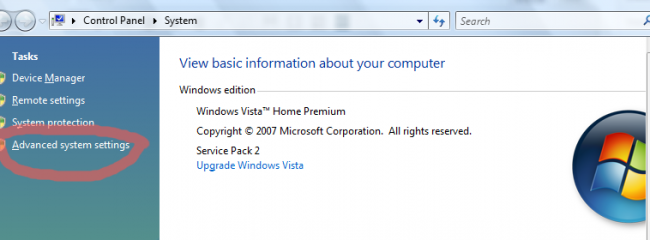
- Click on “Advanced system settings”, then the Settings tab under Performance at the top.
- The “Performance options” page will open. Click on the “Advanced” tab.
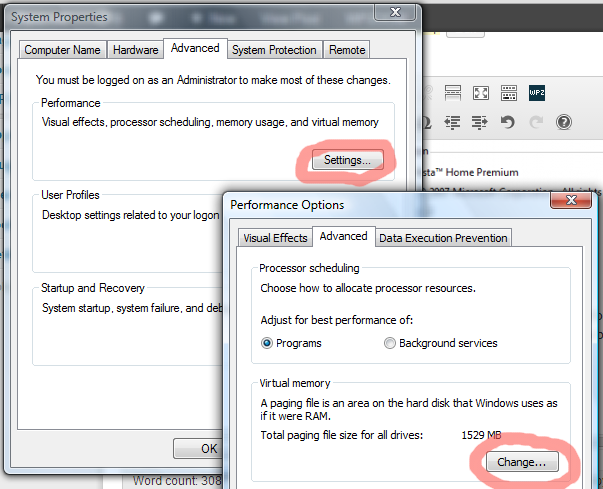
- Now click on the “Change” button under “Virtual memory”.
- You will see the Virtual Memory options page. This controls the size of the paging file.
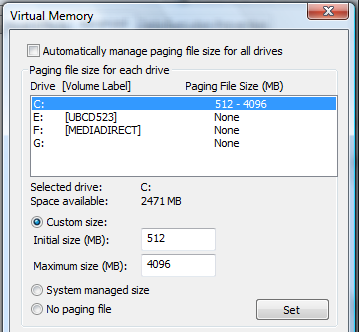
Usually you can tick the top checkbox for “Automatically manage paging size..” and Windows will handle everything itself, as long as you have enough free disk space.
However, you can keep this checked off if you have reasonable values set here.
What are reasonable values here?
See below..
Paging File – Manual settings
Most of the time, you won’t need to use manual settings for virtual memory. However, there are some outlying cases where it might be useful.
One of these might be where you have a limited amount of disk space, and don’t want the available free space to be increasing and decreasing all the time as Windows adjusts the size of the paging file.
Considerations when modifing virtual memory settings:
- Unless you have a lot of memory (at least 8GB) and are using a 64-bit version of Windows, then you should have at least one disk set to use a paging file. This will typically be the C: drive.
- You don’t necessarily need to set a paging file on more than one disk, although it’s possible.
- Recommended minimum size is 512MB for compatibility reasons.
- The Maximum size is a matter of preference, and depends on how many applications you run at the same time, but it’s probably better to set it to at least 4096MB (4 Gig) or higher.
- Using both a SSD and standard hard drive in the same computer?
Moving the paging file to the SSD disk can greatly speed up your system, since page file access can be one of the most frequent reasons for read and write usage of the disk.
This is especially true if you don’t have that much physical RAM installed, or your disk light is frequently lighting up due to disk page file swapping.
There was some concern with earlier SSDs that putting such a highly-used file on the SSD would lead to a shorter lifespan for the solid-state disk, however this is unlikely to be a concern for newer SSDs and the performance boost could be significant.
Has it worked?
Once you’ve either freed up disk space or adjusted your page file settings, you can start the Task Manager again to see what’s happening.
Note that you might have to reboot your computer before doing this if you have changed the virtual memory settings.
Try to start using something that uses up memory, such as a web browser session with a lot of open tabs. If it appears that your page file space is not being exhausted, and you don’t get any popup error messages, then the problem is solved.
To prevent low-memory problems reoccurring, make sure to try to free up enough space on your disk if it’s running low.

Thank you so much for the advice hope it’s work… 🤗🤗🤗 More power.
U are a helping hand and u are great sir thank u
I tried the steps suggested here but it didn’t work. It says to close or delete files but I’m unclear on what files to close or delete. There are files that I’m not sure if I were to close or delete them if they are something I needed (I’m not completely computer illiterate but I’m not the best with it either).
Have you tried using the CCleaner program mentioned in the post?
It should do a good job of finding unnecessary files and cleaning them to free up space. Just uncheck any “Applications” listed in the CCleaner settings dialog as suggested above if you don’t want it to affect browser bookmarks etc.
Where does the post mention a CCLEANER?
Oops, sorry you’re right! The details are in another post here – Free up Disk Space in Windows – 3 Easy & Effective Tools
I have a Win7 Pro 64bit, 32Giga of memory and it is definitely not all in use …yet I get these confusing messages and weird shit is happening…
Still getting the message after your instructions but a little less frequent.
It worked, thank you so much 🙂
it worked well thanhs
it worked thank you
thanks
Is there a way to expand that memory? Aside from taking it to a Geek Squad or other expensive option. Thanks!
Hi Jennifer,
It depends on the model of your computer or laptop. If you have the model number you can post it here.
i have a 2gig ram, what values should i use
Seems odd that this “fix” is more of a “bandage” but doesn’t bother to address the real reason that vista did not have this issue apparently until post ‘new version’ releases… Its obvious if you just think about it that this problem just recently developed so what in the world is suddenly (magically) running on the older system thats using such vast amounts of memory that it cant keep up automatically…. things that make you go hmmmmm
Nothing useful there.
Thanks that worked great – great instructions 🙂
Iit’s interesting that the comments before me are also in the fall of 2014. It’s nice to know I’m not the only one working with a Stone Age computer/program. I haven’t tried this “fix” yet, but I am trusting it will work. Thanks!
Thank you – thorough, clear and very helpful 🙂
Sir, you are a legend…
THANK YOU OMG THANK YOU